David Ricardos Theory Of Free Trade. There are huge advantages for developing the international trade with this classic model.
 Pdf An Evaluation Of David Ricardo S Theory Of Comparative Costs Direct And Indirect Critiques
Pdf An Evaluation Of David Ricardo S Theory Of Comparative Costs Direct And Indirect Critiques
According to this theory trade was zero-sum gain that is gains by one country and loss by another.

David ricardo theory of free international trade. In 1817 David Ricardo an English political economist contributed theory of comparative advantage in his book Principles of Political Economy and Taxation. It encourages the free flow of goods and services between nations without any discrimination. Free trade is an international trade policy that lowers trade barriers such as tariffs and quotas stimulates trade activities between countries and limits government intervention.
Ricardos theory pleads the case for free trade. Intro – Classical Theory of International Trade. The idea is this.
David Ricardo developed this international trade theory based in comparative advantage and specialization two concepts that broke with mercantilism that until then was the ruling economic doctrine. A country that trades for products it can get at lower cost from another country is. The objective of this article is to address the question of international trade under the light of the theory of long run equilibrium prices.
Ricardo assumed that in both countries two goods are producible and actually are produced. It helps explain how trade benefits the world if there is a situation ensures one of the countries can produce both the commodities at a lower cost compared to its trading partner. David Ricardo Theory of Free International Trade Few ideas have been as widely accepted by economists and as roundly rejected by many other people as the doctrine of free international trade.
The most efficient and productive pattern of specialization occurs when people concentrate on. Free trade by increasing the general mass of production diffuses general benefit and binds together by one common tie of interest and intercourse the universal society of nations throughout the civilised world. Adam Smith and David Ricardo gave the classical theories of international trade.
David Ricardo in 1817 has given the comparative advantage theory. Under a system of perfectly free commerce Ricardo wrote each country naturally devotes its capital and labour to such employments as. Ricardos argument in favour of free trade has also been attacked by those who believe trade restriction can be necessary for the economic development of a nation.
Ricardo made a very strong statement about the advantages of free trade at a time when it was a politically charged issue. Economists base their acceptance of the mutual benefits from such trade on a concept called comparative advantage. The theory is most closely associ-.
He stresses that free-trade is the pre-requisite of gains and improvement of worlds welfare. Ricardo like Adam Smith believed free trade would overcome many of the issues connected with Mercantilist economics. From Mercantilism to Free Trade.
David Ricardo explained the reason of international trade under different efficient of labor production. Comparative advantage David Ricardo Adam Smith international trade theory division of labor free trade. Later economists like David Ricardo took the idea of specialisation and refined it into a theory of why free trade would supposedly improve everyones welfare because it led to specialisation between countries.
Theory of International Trade Advanced by David Ricardo. Economics was now more than a theory about the local butcher baker and brewer. Process of reassessment of Smiths contributions to international trade theory further strengthening the view that he was indeed a great international trade theorist.
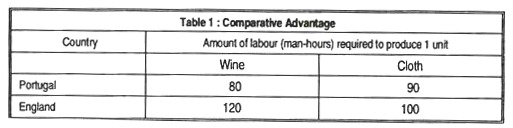
Comparative advantage economic theory first developed by 19th-century British economist David Ricardo that attributed the cause and benefits of international trade to the differences in the relative opportunity costs costs in terms of other goods given up of producing the same commodities among countries. According to the theories given by them when a country enters in foreign trade it benefits from specialization and efficient resource allocation. He introduced this theory for the first time in his book On the Principles of Political Economy and Taxation 1817 using a simple numerical example concerning the trade between Portugal and the England in the following way.
Comparative advantage theory was developed by David Ricardo. It is one of the oldest international trade theory which was developed in 1630. Ricardo also opposed the protectionist Corn Laws which restricted imports of wheat.
Particular attention is given to the principle of comparative advantage and the relationship between free trade and efficiency. In Ricardos theory which was based on the labour theory of value in effect. In the post Napoleonic era England switched from mercantilism to free trade or a closer semblance of free markets and a free movement of labor and capital it reached its gilded age.
This theory of comparative advantage also called comparative cost theory is regarded as the classical theory of international trade. Moreover this theory has drawback and given way to Adam Smiths theory of absolute advantage and David Ricardos theory of comparative advantage both the theory justified that trade is a positive-sum gain that is benefits to all countries. David Ricardo is the starting point for the economic analysis of international trade.
Firstly this model comes from the law of comparative advantage and help the United Kingdom got the solution to the grain crisis from 1815. According to this theory If a country cannot produce goods more efficiently than other countries then it should only produce such goods in which it is most efficient. The foreign trade also helps in bringing new technologies and skills that lead to higher productivity.
In arguing for free trade Ricardo formulated the idea of comparative costs today called comparative advantage a very subtle idea that is the main basis for most economists belief in free trade today. Utsa Patnaik claims that Ricardian theory of international trade contains a logical fallacy. David Ricardo 17721823 was a classical economist best known for his theory on wages and profit the labor theory of value the theory of comparative advantage and the theory of rents.
 Global Economy And Global Economic Governance Intro Online Presentation
Global Economy And Global Economic Governance Intro Online Presentation
 Adam Smith Theory Of International Trade
Adam Smith Theory Of International Trade
 Pdf Reconciling Ricardo S Comparative Advantage With Smith S Productivity Theory
Pdf Reconciling Ricardo S Comparative Advantage With Smith S Productivity Theory
 Comparative Advantage International Trade Theory Economics Online Economics Online
Comparative Advantage International Trade Theory Economics Online Economics Online
 Influence Of David Ricardo S Theory Of Comparative Advantage On Inter
Influence Of David Ricardo S Theory Of Comparative Advantage On Inter
 Ricardian Theory Of Comparative Cost Economics
Ricardian Theory Of Comparative Cost Economics
 Pdf Comparative Advantage And The Labor Theory Of Value
Pdf Comparative Advantage And The Labor Theory Of Value
Https Pure Hud Ac Uk Files 14132571 David Ricardo S Comparative Trade Theory Pdf
 Comparative Advantage Definition Economics Facts Britannica
Comparative Advantage Definition Economics Facts Britannica
 Essay On The Influence Of A Low Price Of Corn On The Profits Of Stock Work By Ricardo Britannica
Essay On The Influence Of A Low Price Of Corn On The Profits Of Stock Work By Ricardo Britannica
 Pdf David Ricardo S Comparative Advantage And Developing Countries Myth And Reality
Pdf David Ricardo S Comparative Advantage And Developing Countries Myth And Reality
 Classical Theory Of International Trade 2 1 Introduction Historical Approach To Examine The Development Of International Trade Theory Mercantilism Ppt Download
Classical Theory Of International Trade 2 1 Introduction Historical Approach To Examine The Development Of International Trade Theory Mercantilism Ppt Download
 Economic Theories David Ricardo Comparative Advantage Ppt Download
Economic Theories David Ricardo Comparative Advantage Ppt Download
 Pdf Ricardo S Numerical Example Versus Ricardian Trade Model A Comparison Of Two Distinct Notions Of Comparative Advantage
Pdf Ricardo S Numerical Example Versus Ricardian Trade Model A Comparison Of Two Distinct Notions Of Comparative Advantage
 Chapter 5 Learning Objectives Factors Explaining International Trade Patterns Differences In Productivity Differences In Factor Endowment International Ppt Download
Chapter 5 Learning Objectives Factors Explaining International Trade Patterns Differences In Productivity Differences In Factor Endowment International Ppt Download





